Smart Irrigation System
Overwatering is the result of inefficiencies in traditional irrigation methods and systems; up to 50% of this water is wasted. A time-based irrigation system, for example, wastes water and causes overwatering because it will continue to run even on rainy days.
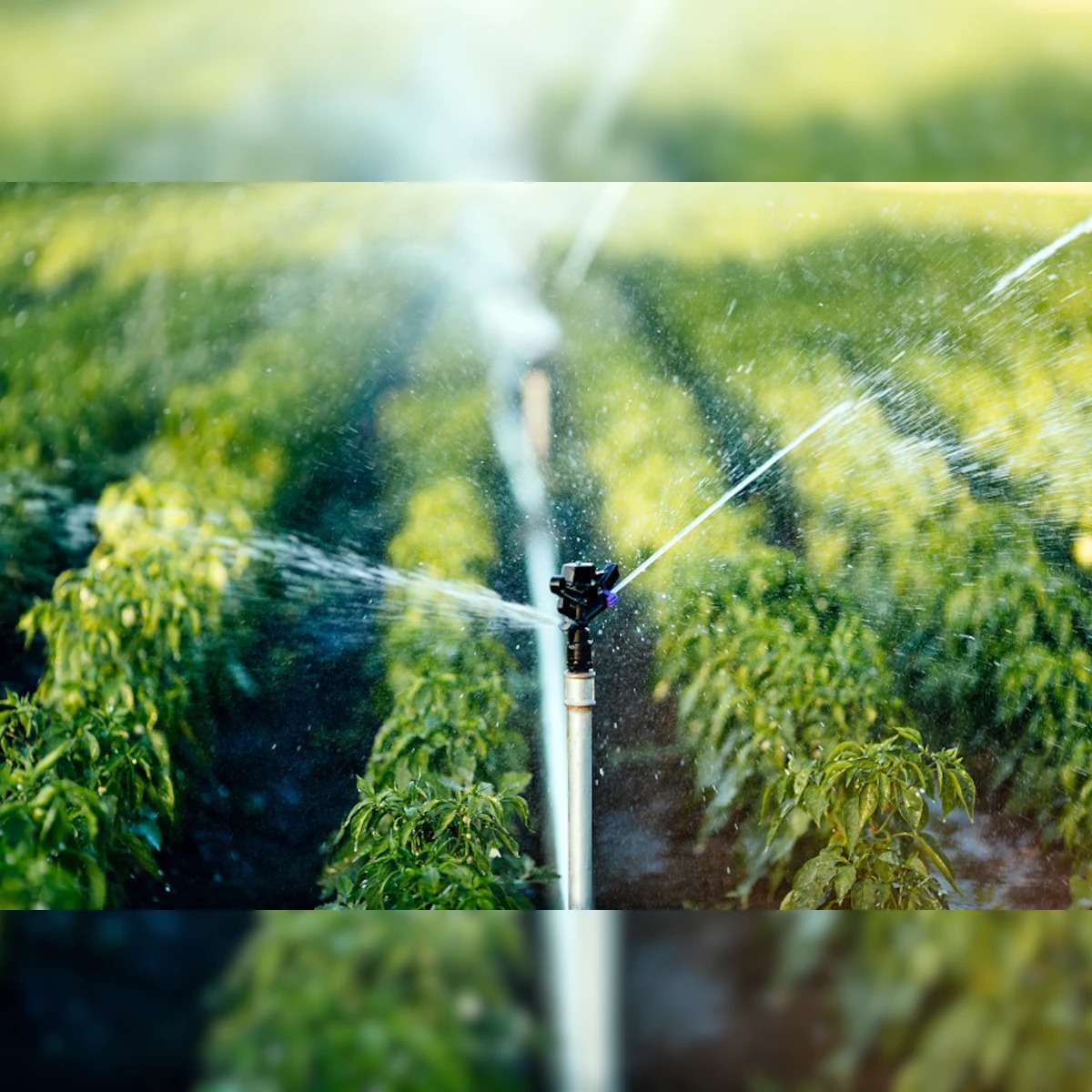
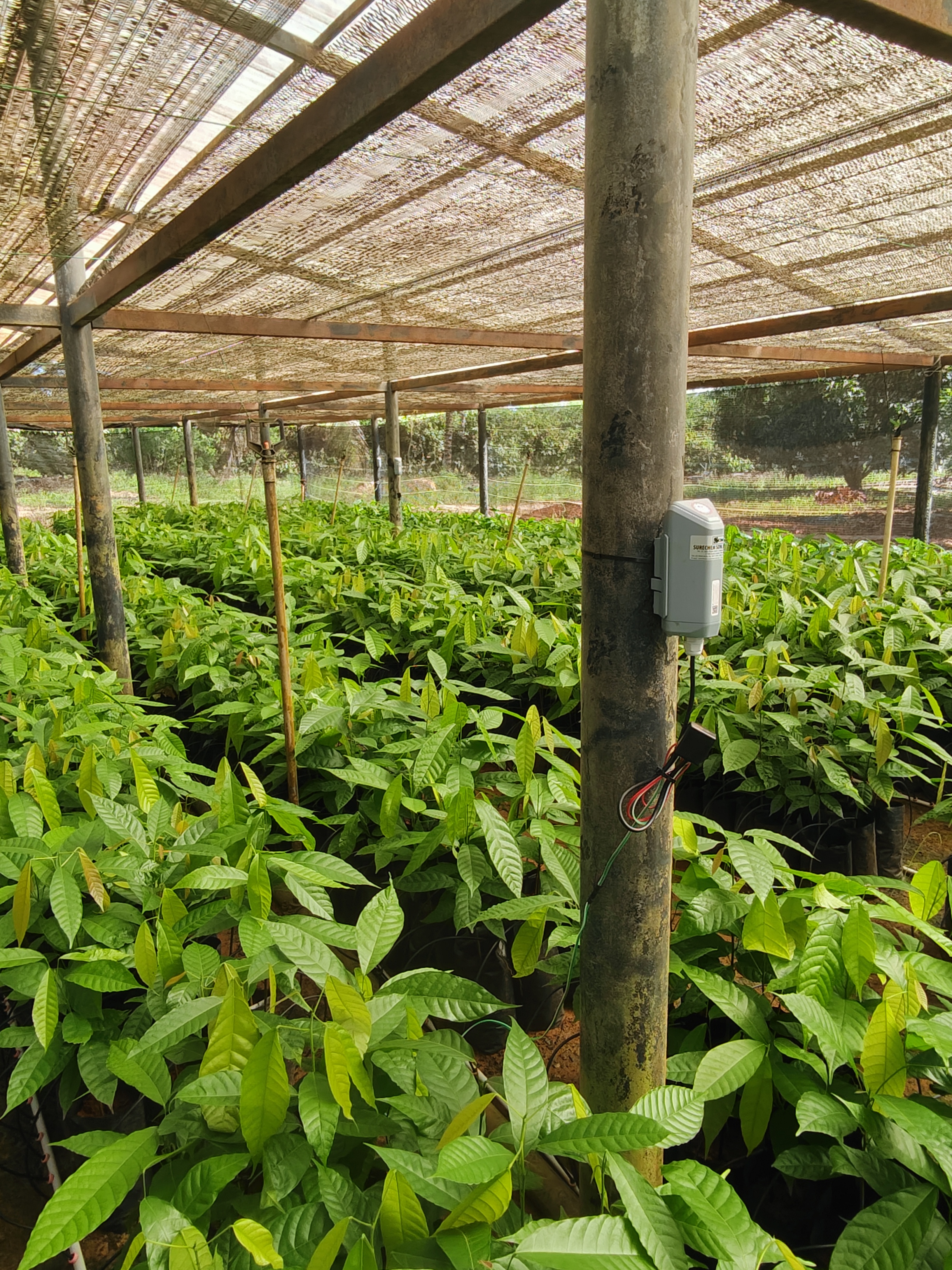
Surechem's Smart Irrigation System can be integrated into existing or new irrigation controllers and uses advanced monitoring technology to monitor moisture-related conditions on your property and automatically adjust watering to optimal levels.
Weather-based smart irrigation technology and soil moisture-based smart irrigation technology are the two types of smart irrigation technology. Both of these can assist you in conserving water, but there are some notable differences.
Weather-based Smart Irrigation
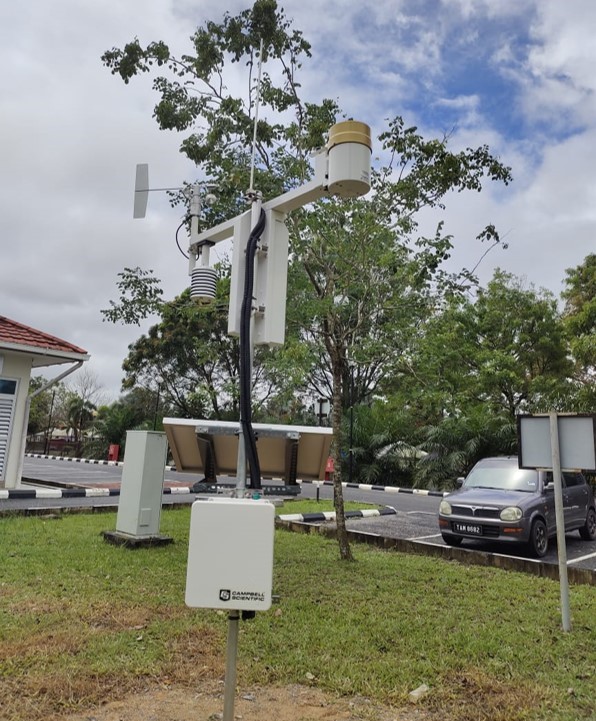
Weather-based smart irrigation system mainly refer to local weather data and evapotranspiration (ET) to adjust irrigation schedules. The combination of evaporation or amount of water lost from the soil surface and transpiration by plant materials is known as evapotranspiration. These collect local weather data are use to adjust irrigation run-time to ensure that the landscape receives the proper amount of water. Temperature, wind, solar radiation, and humidity are the four weather parameters used by ET weather data. It is the most accurate method of calculating landscape water requirements.
The Campbell Scientific Evapotranspiration Monitoring Station ET107 is an automated weather station designed for irrigation scheduling in turf grass and commercial agriculture applications. The station calculates potential evapotranspiration (ET) to aid in the development of an irrigation schedule that provides sufficient water without overwatering.
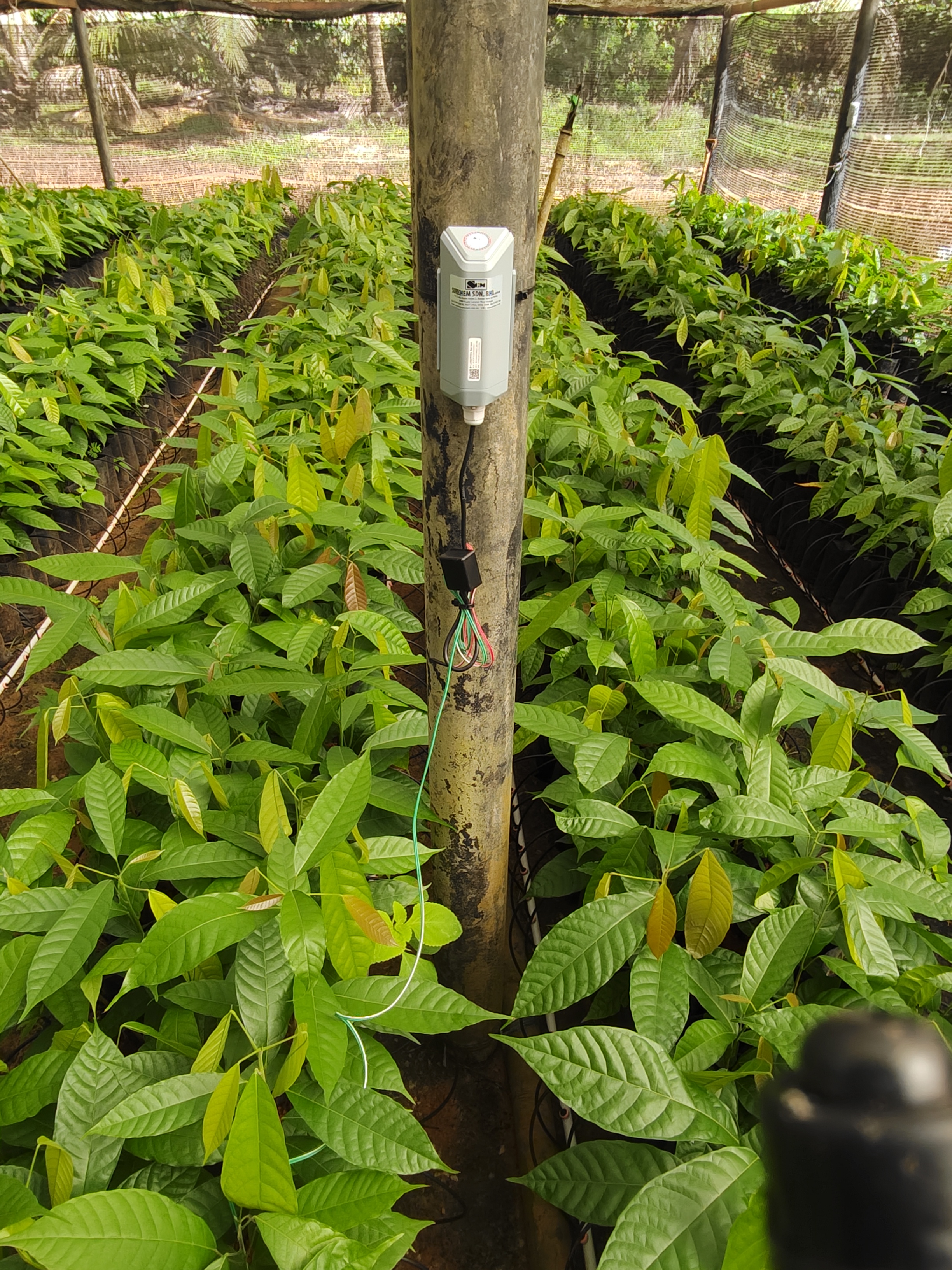
Moisture-based Smart Irrigation
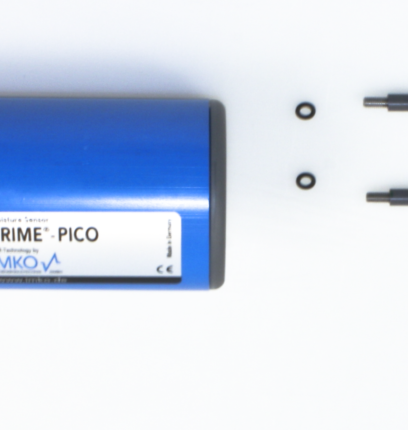
Soil moisture sensors are used in soil moisture-based smart irrigation systems to measure the actual moisture content of the soil. To obtain an average soil moisture reading in an area, multiple soil moisture stations can be installed on your property. Irrigation can then be automatically triggered when the average soil moisture value reaches a user-defined threshold. Other sensors, such as water level sensors, can be integrated alongside to monitor water level in an irrigation water tank, reservoir, or groundwater borehole.